Vitassay
Rapid Test
Vitassay H. pylori
Ref.
| Referencia | 7355020 |
|---|
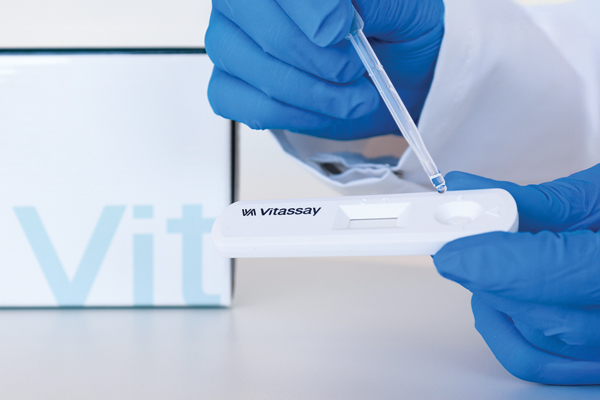
Diseño fácil de usar
Formato ergonómico
Resultados rápidos: 2 mins manipulación y 10 min tiempo de lectura
Lectura sencilla: Línea Verde de Control & Línea Roja de Test
Características del Kit
25 tests/kit
Posibilidad de incluir Control Positivo & Negativo
Seleccione su idioma para descargar el instructivo de este producto:
Descargas Disponibles: